File size: 6,850 Bytes
3d69c05 b43baac 3d69c05 b43baac 3d69c05 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 |
---
language:
- multilingual
license: other
license_name: kwaipilot-license
license_link: LICENSE
library_name: transformers
---
<div align="center">
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Anditty/OASIS/refs/heads/main/Group.svg" width="60%" alt="Kwaipilot" />
</div>
<hr>
<div align="center" style="line-height: 1;">
<a href="https://huggingface.co/Kwaipilot/KAT-V1-40B" target="_blank">
<img alt="Hugging Face" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/HuggingFace-fcd022?style=for-the-badge&logo=huggingface&logoColor=000&labelColor"/>
</a>
<a href="https://arxiv.org/pdf/2507.08297" target="_blank">
<img alt="arXiv" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/arXiv-2507.08297-b31b1b.svg?style=for-the-badge"/>
</a>
</div>
# News
- Kwaipilot-AutoThink ranks first among all open-source models on [LiveCodeBench Pro](https://livecodebenchpro.com/), a challenging benchmark explicitly designed to prevent data leakage, and even surpasses strong proprietary systems such as Seed and o3-mini.
***
# Introduction
**KAT (Kwaipilot-AutoThink)** is an open-source large-language model that mitigates *over-thinking* by learning **when** to produce explicit chain-of-thought and **when** to answer directly.
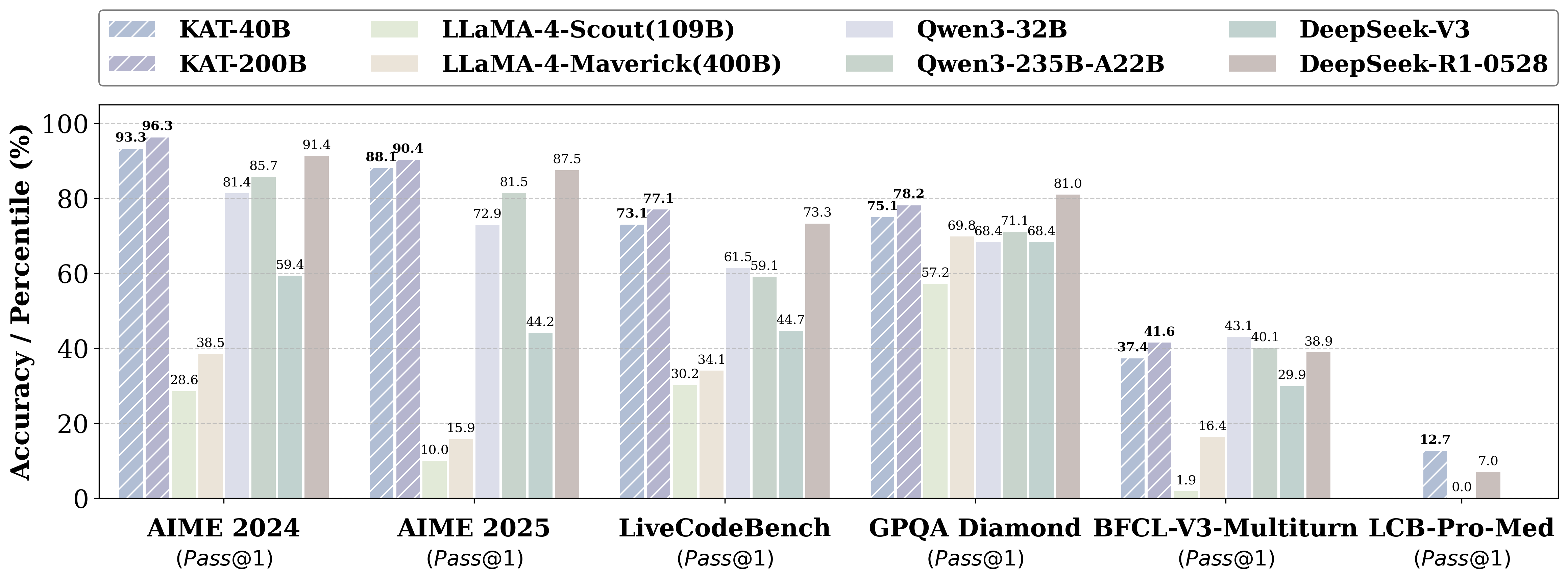
Its development follows a concise two-stage training pipeline:
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th style="text-align:left; width:18%;">Stage</th>
<th style="text-align:left;">Core Idea</th>
<th style="text-align:left;">Key Techniques</th>
<th style="text-align:left;">Outcome</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td><strong>1. Pre-training</strong></td>
<td>Inject knowledge while separating “reasoning” from “direct answering”.</td>
<td>
<em>Dual-regime data</em><br>
• <strong>Think-off</strong> queries labeled via a custom tagging system.<br>
• <strong>Think-on</strong> queries generated by a multi-agent solver.<br><br>
<em>Knowledge Distillation + Multi-Token Prediction</em> for fine-grained utility.
</td>
<td>Base model attains strong factual and reasoning skills without full-scale pre-training costs.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><strong>2. Post-training</strong></td>
<td>Make reasoning optional and efficient.</td>
<td>
<em>Cold-start AutoThink</em> — majority vote sets the initial thinking mode.<br>
<em>Step-SRPO</em> — intermediate supervision rewards correct <strong>mode selection</strong> and <strong>answer accuracy</strong> under that mode.
</td>
<td>Model triggers CoT only when beneficial, reducing token use and speeding inference.</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
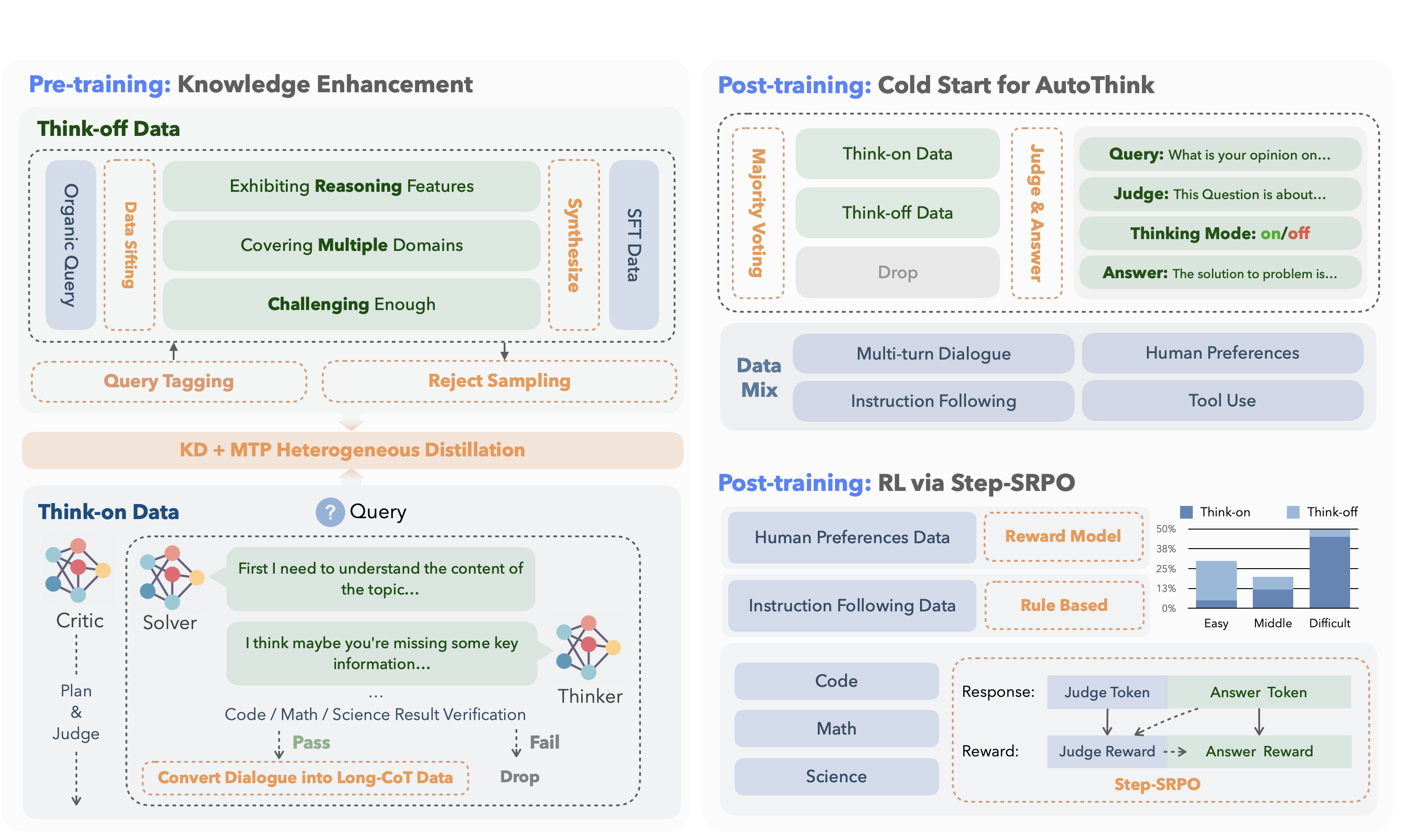
***
# Data Format
KAT produces responses in a **structured template** that makes the reasoning path explicit and machine-parsable.
Two modes are supported:
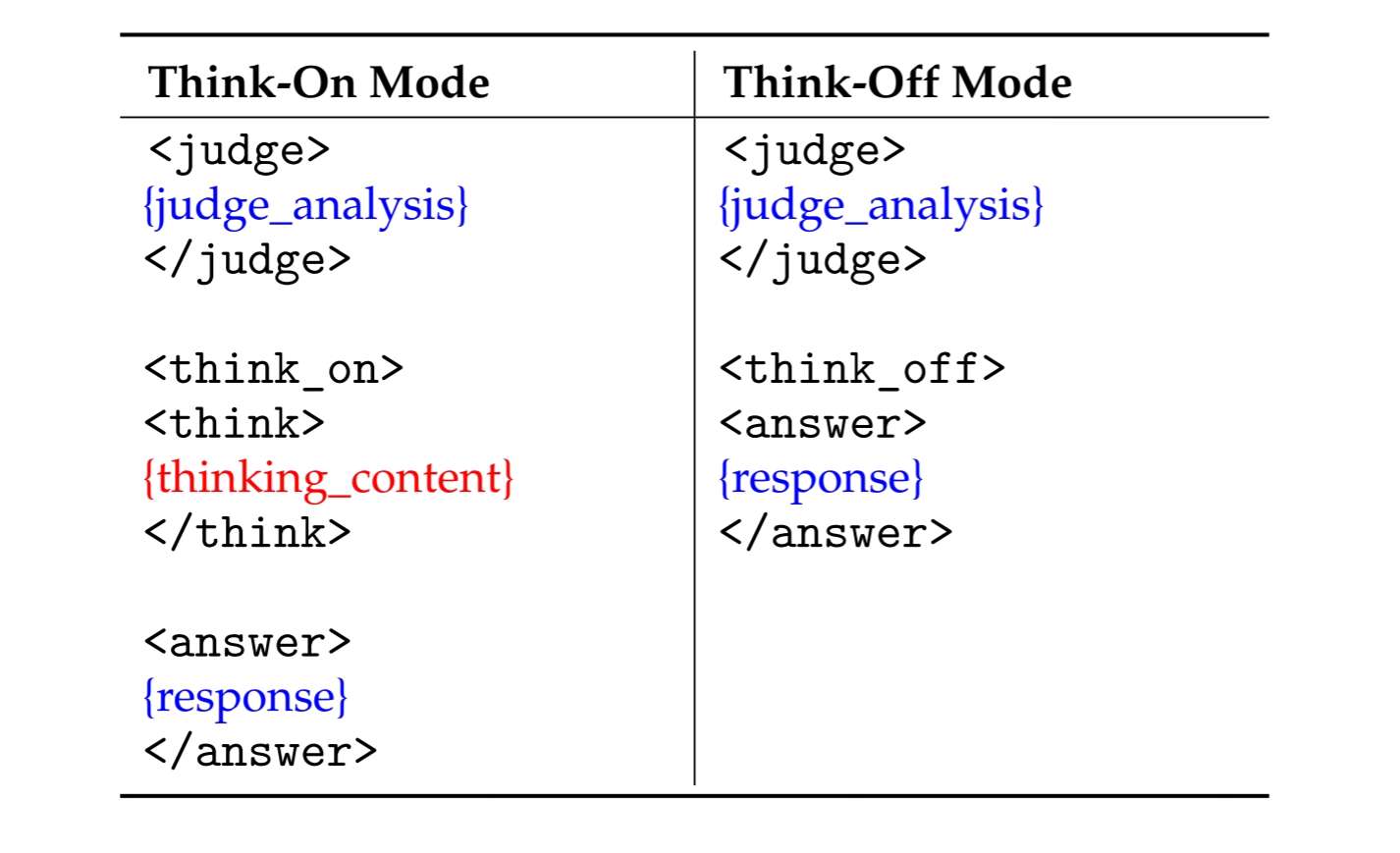
## Special Tokens
| Token | Description |
|-------|-------------|
| `<judge>` | Analyzes the input to decide whether explicit reasoning is needed. |
| `<think_on>` / `<think_off>` | Indicates whether reasoning is **activated** (“on”) or **skipped** (“off”). |
| `<think>` | Marks the start of the chain-of-thought segment when `think_on` is chosen. |
| `<answer>` | Marks the start of the final user-facing answer. |
***
# 🔧 Quick Start
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
model_name = "Kwaipilot/KAT-V1-40B"
# load the tokenizer and the model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
# prepare the model input
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# conduct text completion
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=65536,
temperature=0.6,
top_p=0.95,
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
print("prompt:\n", prompt)
print("content:\n", content)
"""
prompt:
Give me a short introduction to large language model.
content:
<judge>
The user's request is to provide a concise factual introduction to large language models, which involves retrieving and summarizing basic information. This task is straightforward as it only requires recalling and presenting well-known details without deeper analysis. No complex reasoning is needed here—just a simple explanation will suffice.
</judge>
<think_off>
<answer>
A **Large Language Model (LLM)** is an advanced AI system trained on vast amounts of text data to understand, generate, and process human-like language. Here’s a concise introduction:
### Key Points:
1. **Training**: Trained on diverse text sources (books, websites, etc.) using deep learning.
2. **Capabilities**:
- Answer questions, generate text, summarize content, translate languages.
- Understand context, sentiment, and nuances in language.
3. **Architecture**: Often based on **transformer models** (e.g., BERT, GPT, LLaMA).
4. **Scale**: Billions of parameters, requiring massive computational resources.
5. **Applications**: Chatbots, content creation, coding assistance, research, and more.
### Examples:
- **OpenAI’s GPT-4**: Powers ChatGPT.
- **Google’s Gemini**: Used in Bard.
- **Meta’s LLaMA**: Open-source alternative.
### Challenges:
- **Bias**: Can reflect biases in training data.
- **Accuracy**: May hallucinate "facts" not grounded in reality.
- **Ethics**: Raises concerns about misinformation and job displacement.
LLMs represent a leap forward in natural language processing, enabling machines to interact with humans in increasingly sophisticated ways. 🌐🤖
</answer>
"""
```
***
# Future Releases
Looking ahead, we will publish a companion paper that fully documents the **AutoThink training framework**, covering:
* Cold-start initialization procedures
* Reinforcement-learning (Step-SRPO) strategies
* Data curation and reward design details
At the same time, we will open-source:
* **Training resources** – the curated dual-regime datasets and RL codebase
* **Model suite** – checkpoints at 1.5B, 7B, and 13B parameters, all trained with AutoThink gating |