|
|
--- |
|
|
language: |
|
|
- multilingual |
|
|
license: other |
|
|
license_name: kwaipilot-license |
|
|
license_link: LICENSE |
|
|
library_name: transformers |
|
|
--- |
|
|
<div align="center"> |
|
|
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Anditty/OASIS/refs/heads/main/Group.svg" width="60%" alt="Kwaipilot" /> |
|
|
</div> |
|
|
|
|
|
<hr> |
|
|
|
|
|
<div align="center" style="line-height: 1;"> |
|
|
<a href="https://huggingface.co/Kwaipilot/KAT-V1-40B" target="_blank"> |
|
|
<img alt="Hugging Face" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/HuggingFace-fcd022?style=for-the-badge&logo=huggingface&logoColor=000&labelColor"/> |
|
|
</a> |
|
|
|
|
|
<a href="https://arxiv.org/pdf/2507.08297" target="_blank"> |
|
|
<img alt="arXiv" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/arXiv-2507.08297-b31b1b.svg?style=for-the-badge"/> |
|
|
</a> |
|
|
</div> |
|
|
|
|
|
# News |
|
|
|
|
|
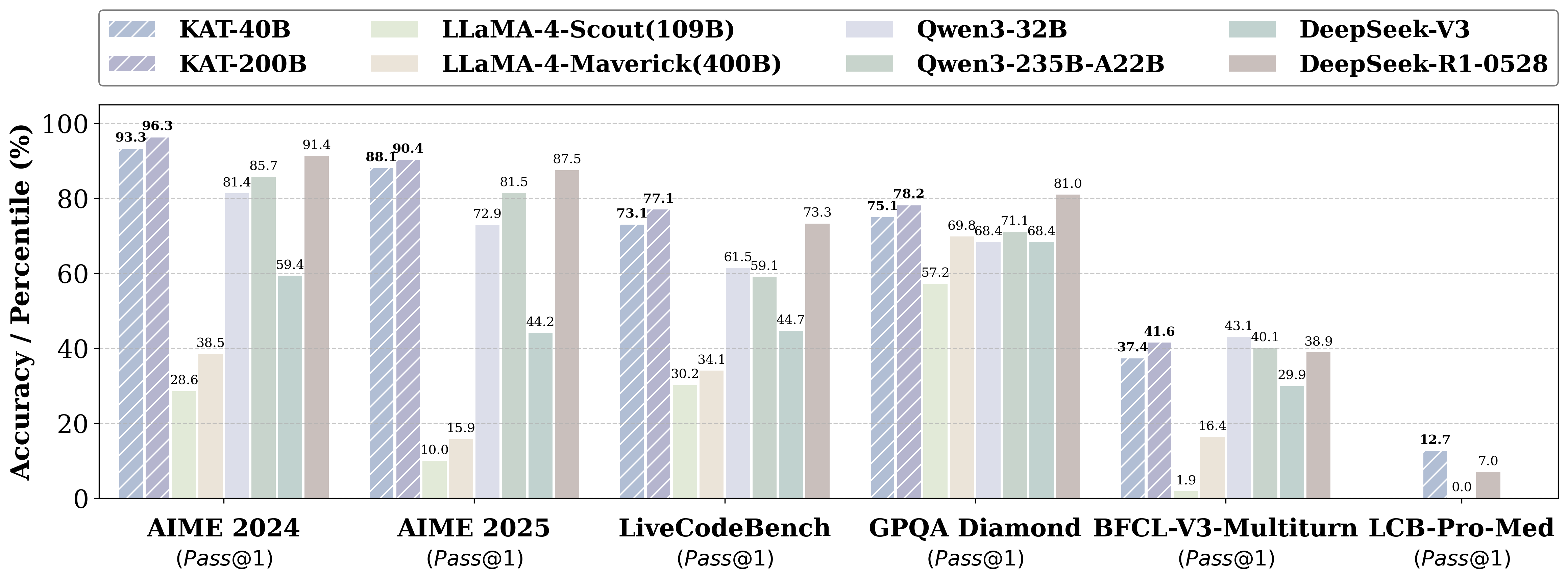
- Kwaipilot-AutoThink ranks first among all open-source models on [LiveCodeBench Pro](https://livecodebenchpro.com/), a challenging benchmark explicitly designed to prevent data leakage, and even surpasses strong proprietary systems such as Seed and o3-mini. |
|
|
|
|
|
*** |
|
|
|
|
|
# Introduction |
|
|
|
|
|
**KAT (Kwaipilot-AutoThink)** is an open-source large-language model that mitigates *over-thinking* by learning **when** to produce explicit chain-of-thought and **when** to answer directly. |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
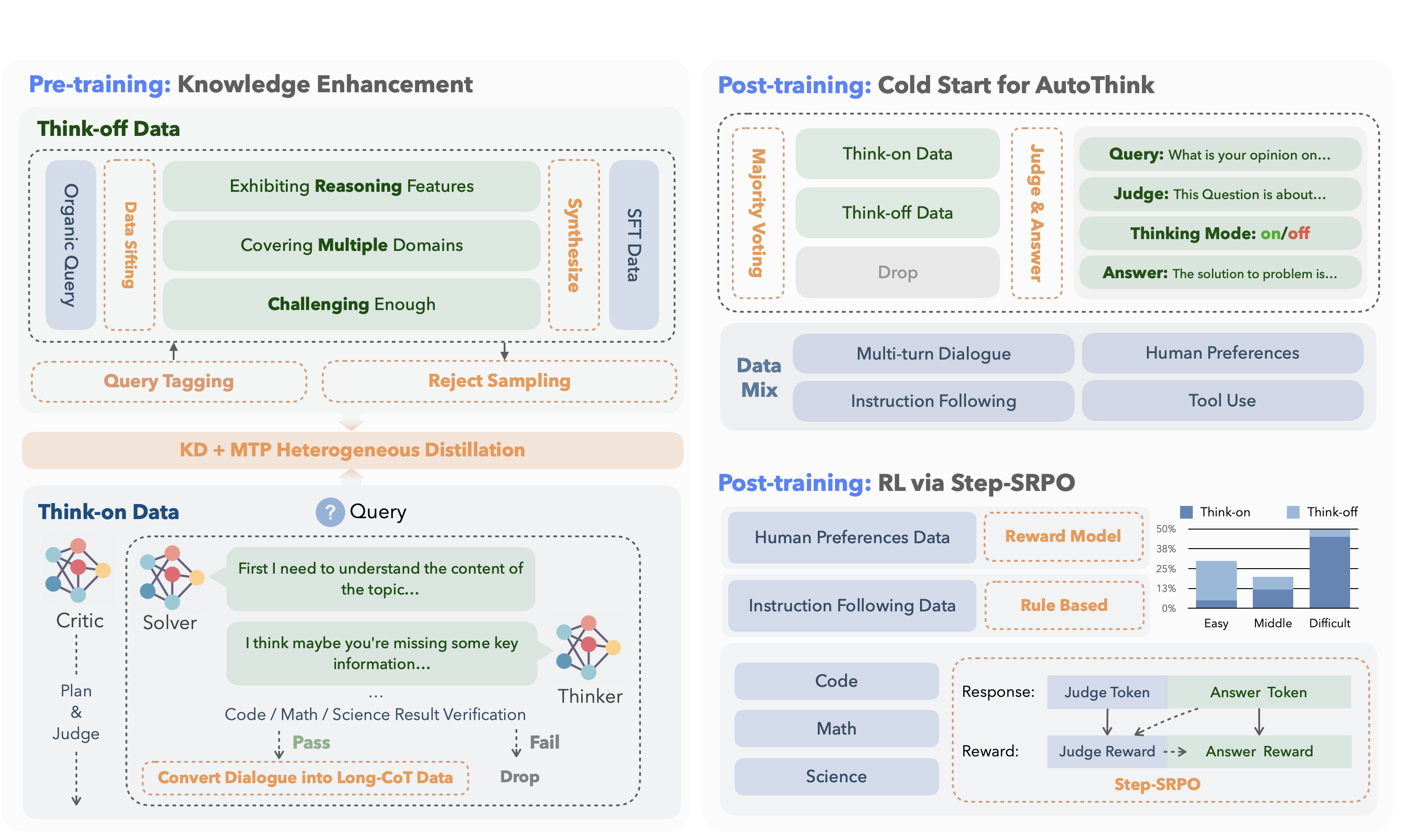
Its development follows a concise two-stage training pipeline: |
|
|
|
|
|
<table> |
|
|
<thead> |
|
|
<tr> |
|
|
<th style="text-align:left; width:18%;">Stage</th> |
|
|
<th style="text-align:left;">Core Idea</th> |
|
|
<th style="text-align:left;">Key Techniques</th> |
|
|
<th style="text-align:left;">Outcome</th> |
|
|
</tr> |
|
|
</thead> |
|
|
<tbody> |
|
|
<tr> |
|
|
<td><strong>1. Pre-training</strong></td> |
|
|
<td>Inject knowledge while separating “reasoning” from “direct answering”.</td> |
|
|
<td> |
|
|
<em>Dual-regime data</em><br> |
|
|
• <strong>Think-off</strong> queries labeled via a custom tagging system.<br> |
|
|
• <strong>Think-on</strong> queries generated by a multi-agent solver.<br><br> |
|
|
<em>Knowledge Distillation + Multi-Token Prediction</em> for fine-grained utility. |
|
|
</td> |
|
|
<td>Base model attains strong factual and reasoning skills without full-scale pre-training costs.</td> |
|
|
</tr> |
|
|
<tr> |
|
|
<td><strong>2. Post-training</strong></td> |
|
|
<td>Make reasoning optional and efficient.</td> |
|
|
<td> |
|
|
<em>Cold-start AutoThink</em> — majority vote sets the initial thinking mode.<br> |
|
|
<em>Step-SRPO</em> — intermediate supervision rewards correct <strong>mode selection</strong> and <strong>answer accuracy</strong> under that mode. |
|
|
</td> |
|
|
<td>Model triggers CoT only when beneficial, reducing token use and speeding inference.</td> |
|
|
</tr> |
|
|
</tbody> |
|
|
</table> |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*** |
|
|
|
|
|
# Data Format |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
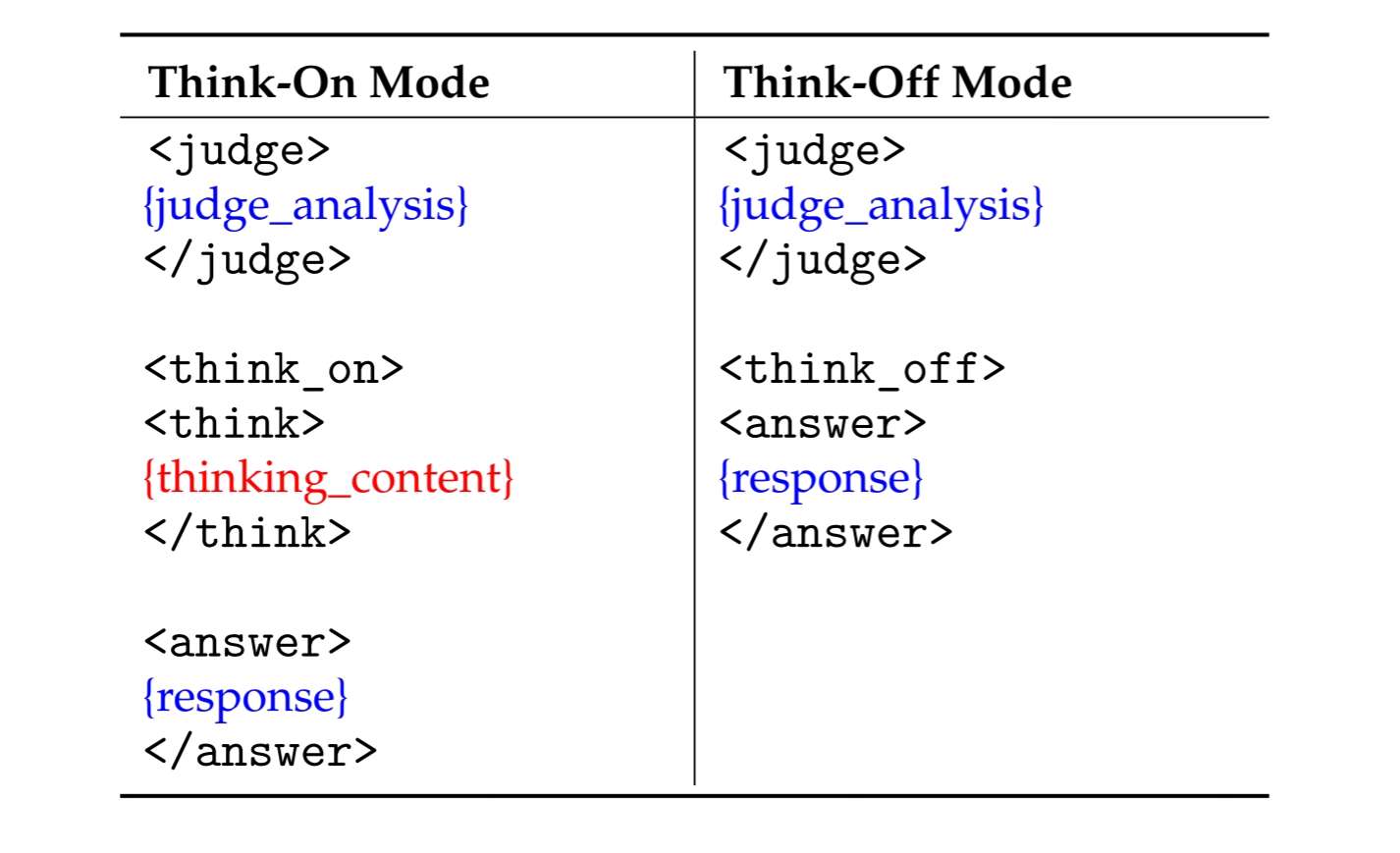
KAT produces responses in a **structured template** that makes the reasoning path explicit and machine-parsable. |
|
|
Two modes are supported: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Special Tokens |
|
|
|
|
|
| Token | Description | |
|
|
|-------|-------------| |
|
|
| `<judge>` | Analyzes the input to decide whether explicit reasoning is needed. | |
|
|
| `<think_on>` / `<think_off>` | Indicates whether reasoning is **activated** (“on”) or **skipped** (“off”). | |
|
|
| `<think>` | Marks the start of the chain-of-thought segment when `think_on` is chosen. | |
|
|
| `<answer>` | Marks the start of the final user-facing answer. | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*** |
|
|
|
|
|
# 🔧 Quick Start |
|
|
|
|
|
```python |
|
|
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM |
|
|
|
|
|
model_name = "Kwaipilot/KAT-V1-40B" |
|
|
|
|
|
# load the tokenizer and the model |
|
|
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True) |
|
|
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained( |
|
|
model_name, |
|
|
torch_dtype="auto", |
|
|
device_map="auto" |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
# prepare the model input |
|
|
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model." |
|
|
messages = [ |
|
|
{"role": "user", "content": prompt} |
|
|
] |
|
|
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template( |
|
|
messages, |
|
|
tokenize=False, |
|
|
add_generation_prompt=True |
|
|
) |
|
|
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device) |
|
|
|
|
|
# conduct text completion |
|
|
generated_ids = model.generate( |
|
|
**model_inputs, |
|
|
max_new_tokens=65536, |
|
|
temperature=0.6, |
|
|
top_p=0.95, |
|
|
) |
|
|
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist() |
|
|
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n") |
|
|
print("prompt:\n", prompt) |
|
|
print("content:\n", content) |
|
|
""" |
|
|
prompt: |
|
|
Give me a short introduction to large language model. |
|
|
content: |
|
|
<judge> |
|
|
The user's request is to provide a concise factual introduction to large language models, which involves retrieving and summarizing basic information. This task is straightforward as it only requires recalling and presenting well-known details without deeper analysis. No complex reasoning is needed here—just a simple explanation will suffice. |
|
|
</judge> |
|
|
|
|
|
<think_off> |
|
|
<answer> |
|
|
A **Large Language Model (LLM)** is an advanced AI system trained on vast amounts of text data to understand, generate, and process human-like language. Here’s a concise introduction: |
|
|
|
|
|
### Key Points: |
|
|
1. **Training**: Trained on diverse text sources (books, websites, etc.) using deep learning. |
|
|
2. **Capabilities**: |
|
|
- Answer questions, generate text, summarize content, translate languages. |
|
|
- Understand context, sentiment, and nuances in language. |
|
|
3. **Architecture**: Often based on **transformer models** (e.g., BERT, GPT, LLaMA). |
|
|
4. **Scale**: Billions of parameters, requiring massive computational resources. |
|
|
5. **Applications**: Chatbots, content creation, coding assistance, research, and more. |
|
|
|
|
|
### Examples: |
|
|
- **OpenAI’s GPT-4**: Powers ChatGPT. |
|
|
- **Google’s Gemini**: Used in Bard. |
|
|
- **Meta’s LLaMA**: Open-source alternative. |
|
|
|
|
|
### Challenges: |
|
|
- **Bias**: Can reflect biases in training data. |
|
|
- **Accuracy**: May hallucinate "facts" not grounded in reality. |
|
|
- **Ethics**: Raises concerns about misinformation and job displacement. |
|
|
|
|
|
LLMs represent a leap forward in natural language processing, enabling machines to interact with humans in increasingly sophisticated ways. 🌐🤖 |
|
|
</answer> |
|
|
""" |
|
|
``` |
|
|
|
|
|
*** |
|
|
|
|
|
# Future Releases |
|
|
|
|
|
Looking ahead, we will publish a companion paper that fully documents the **AutoThink training framework**, covering: |
|
|
|
|
|
* Cold-start initialization procedures |
|
|
* Reinforcement-learning (Step-SRPO) strategies |
|
|
* Data curation and reward design details |
|
|
|
|
|
At the same time, we will open-source: |
|
|
|
|
|
* **Training resources** – the curated dual-regime datasets and RL codebase |
|
|
* **Model suite** – checkpoints at 1.5B, 7B, and 13B parameters, all trained with AutoThink gating |