File size: 49,946 Bytes
68483c2 1bcd8ba cf823f1 8180839 37181c7 ad3a952 8180839 37181c7 45f7e70 37181c7 45f7e70 d09c742 37181c7 45f7e70 d09c742 37181c7 45f7e70 0c0d736 45f7e70 8180839 0c0d736 11c7a1e bceecd4 3bd4cd4 11c7a1e d2e0e19 9e680b1 bceecd4 05c25ae 33eca92 d403607 d76f618 33eca92 cc068f8 c6de7de ea35945 c6de7de bceecd4 c6de7de bceecd4 c6de7de cc068f8 c6de7de bceecd4 a7f6abf 6d5e41a d76f618 bceecd4 c6de7de 33eca92 5cb5c6b c6de7de dc68f3f 8b3b01c fb668ad e896147 8b3b01c c11e4ce c6de7de 8b3b01c c6de7de 8b3b01c c6de7de fe5faf4 33eca92 3acbbd4 de9c368 33eca92 1a604fd 7afdb71 bd45820 33eca92 de9c368 3acbbd4 33eca92 3acbbd4 02b500d ba5302b 33eca92 ba5302b 191b01b bceecd4 fe5faf4 94cd4d3 fe5faf4 0553d6a fe5faf4 8b3b01c fe5faf4 8b3b01c fe5faf4 bceecd4 ba5302b fe5faf4 ba5302b 33eca92 df22b26 191b01b b61e892 703be4e b61e892 d76f618 6d5e41a d76f618 aea3539 a3a4079 df22b26 aea3539 d76f618 bceecd4 ba5302b fe5faf4 ba5302b 33eca92 02b500d bceecd4 05c25ae df22b26 6d5e41a 0553d6a df22b26 6d5e41a 191b01b 02b500d bceecd4 05c25ae 02b500d 191b01b bceecd4 05c25ae 191b01b bceecd4 05c25ae 191b01b bceecd4 0cea469 191b01b bceecd4 0cea469 191b01b 02b500d bceecd4 05c25ae bceecd4 02b500d 05c25ae ba5302b fbf52be de814c2 fbf52be 02b500d fbf52be 02b500d fbf52be 02b500d fbf52be 8b3b01c fbf52be de814c2 fbf52be 8b3b01c c11e4ce fbf52be 8b3b01c fbf52be 29c715d 02b500d bceecd4 de814c2 fbf52be 02b500d 33eca92 54b0d76 2571a0e 33eca92 2571a0e fe5faf4 02b500d 33eca92 02b500d 33eca92 02b500d bceecd4 33eca92 bceecd4 33eca92 02b500d bceecd4 33eca92 02b500d 33eca92 6e962ee 33eca92 6e962ee 33eca92 6e962ee 33eca92 6e962ee 33eca92 6e962ee 33eca92 6e962ee 33eca92 6e962ee 33eca92 bceecd4 33eca92 02b500d 33eca92 02b500d 33eca92 54b0d76 c6de7de d6ef863 c6de7de d6ef863 82c47ab d6ef863 8b3b01c 82c47ab c6de7de fe5faf4 d6ef863 bceecd4 d6ef863 33eca92 6faaceb 33eca92 8c53afc 014eb5c 8b3b01c ead39ba 014eb5c ead39ba 014eb5c 33eca92 ae4419c 33eca92 ae4419c 33eca92 ae4419c 33eca92 9e680b1 d228382 9e680b1 ae4419c bceecd4 33eca92 3c3f1b5 9a6635a 33eca92 2e056db c11e4ce 2e056db 9f4950c c11e4ce 9f4950c 2e056db bceecd4 2e056db 33eca92 b6db833 bceecd4 b6db833 d6fd606 b6db833 90583bd 5e1537b 90583bd 5e1537b c8208d7 5e1537b 90583bd d1341c2 03dfccd d1341c2 bceecd4 d1341c2 33eca92 e06a7a0 bceecd4 e06a7a0 bceecd4 e06a7a0 b6db833 e06a7a0 8b3b01c e06a7a0 8b3b01c e06a7a0 03dfccd 33eca92 ffb913a 3c3f1b5 ffb913a abfe76a 0bee9e3 abfe76a 0bee9e3 abfe76a 607159b 02b500d 607159b bceecd4 02b500d 607159b bceecd4 607159b bceecd4 02b500d bceecd4 02b500d bceecd4 02b500d bceecd4 02b500d bceecd4 02b500d bceecd4 02b500d bceecd4 570f425 bceecd4 570f425 7b8ac1f bceecd4 7b8ac1f 3c3f1b5 05c25ae 3c3f1b5 11c7a1e 3c3f1b5 9a6635a af7f5dd 3c3f1b5 bceecd4 3c3f1b5 bceecd4 3c3f1b5 02b500d 3c3f1b5 02b500d 3c3f1b5 11c7a1e af7f5dd 11c7a1e 05c25ae c6de7de bceecd4 c6de7de bceecd4 df22b26 c6de7de bceecd4 df22b26 ba5302b df22b26 c6de7de bceecd4 ba5302b df22b26 f0c9ea0 bceecd4 c6de7de ba5302b df22b26 c6de7de df22b26 c6de7de bceecd4 ba5302b fe5faf4 c6de7de f0c9ea0 11c7a1e c6de7de df22b26 bceecd4 1971f8d fe5faf4 1971f8d bceecd4 1971f8d ba5302b df22b26 1971f8d bceecd4 ba5302b fe5faf4 1971f8d bceecd4 1971f8d ba5302b df22b26 1971f8d df22b26 1971f8d bceecd4 ba5302b fe5faf4 1971f8d df22b26 ba5302b df22b26 1971f8d df22b26 1971f8d bceecd4 ba5302b 1971f8d bceecd4 1971f8d ba5302b df22b26 1971f8d df22b26 1971f8d bceecd4 ba5302b 9410eb7 1a15656 925700e 6f28f12 c6de7de 146956b c6de7de df22b26 c6de7de bceecd4 6f28f12 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 692 693 694 695 696 697 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716 717 718 719 720 721 722 723 724 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 750 751 752 753 754 755 756 757 758 759 760 761 762 763 764 765 766 767 768 769 770 771 772 773 774 775 776 777 778 779 780 781 782 783 784 785 786 787 788 789 790 791 792 793 794 795 796 797 798 799 800 801 802 803 804 805 806 807 808 809 810 811 812 813 814 815 816 817 818 819 820 821 822 823 824 825 826 827 828 829 830 831 832 833 834 835 836 837 838 839 840 841 842 843 844 845 846 847 848 849 850 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 863 864 865 866 867 868 869 870 871 872 873 874 875 876 877 878 879 880 881 882 883 884 885 886 887 888 889 890 891 892 893 894 895 896 897 898 899 900 901 902 903 904 905 906 907 908 909 910 911 912 913 914 915 916 917 918 919 920 921 922 923 924 925 926 927 928 929 930 931 932 933 934 935 936 937 938 939 940 941 942 943 944 945 946 947 948 949 950 951 952 953 954 955 956 957 958 959 960 961 962 963 964 965 966 967 968 969 970 971 972 973 974 975 976 977 978 979 980 981 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 991 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 1000 1001 1002 1003 1004 1005 1006 1007 1008 1009 1010 1011 1012 1013 1014 1015 1016 1017 1018 1019 1020 1021 1022 1023 1024 1025 1026 1027 1028 1029 1030 1031 1032 1033 1034 1035 1036 1037 1038 1039 1040 1041 1042 1043 1044 1045 1046 1047 1048 1049 1050 1051 1052 1053 1054 1055 1056 1057 1058 1059 1060 1061 1062 1063 1064 1065 1066 1067 1068 1069 1070 1071 1072 1073 1074 1075 1076 1077 1078 1079 1080 1081 1082 1083 1084 1085 1086 1087 1088 1089 1090 1091 1092 1093 1094 1095 1096 1097 1098 1099 1100 1101 1102 1103 1104 1105 1106 1107 1108 1109 1110 1111 1112 1113 1114 1115 1116 1117 1118 1119 1120 1121 1122 1123 1124 1125 1126 1127 1128 1129 1130 1131 1132 1133 1134 1135 1136 1137 1138 1139 1140 1141 1142 1143 1144 1145 1146 1147 1148 1149 1150 1151 1152 1153 1154 1155 1156 1157 1158 1159 1160 1161 1162 1163 1164 1165 1166 1167 1168 1169 1170 1171 1172 1173 1174 1175 1176 1177 1178 1179 1180 1181 1182 1183 1184 1185 1186 1187 1188 1189 1190 1191 1192 1193 1194 1195 1196 1197 1198 1199 1200 1201 1202 1203 1204 1205 1206 1207 1208 1209 1210 1211 1212 1213 1214 1215 1216 1217 1218 1219 1220 1221 1222 1223 1224 1225 1226 1227 1228 1229 1230 1231 1232 1233 1234 1235 1236 1237 1238 1239 1240 1241 1242 1243 1244 1245 1246 1247 1248 1249 1250 1251 1252 1253 1254 1255 1256 1257 1258 1259 1260 1261 1262 1263 1264 1265 1266 1267 1268 1269 1270 1271 1272 1273 1274 1275 1276 1277 1278 1279 1280 1281 1282 1283 1284 1285 1286 1287 1288 1289 1290 1291 1292 1293 1294 1295 1296 1297 1298 1299 1300 1301 1302 1303 1304 1305 1306 1307 1308 1309 1310 1311 1312 1313 1314 1315 1316 1317 1318 1319 1320 1321 1322 1323 1324 1325 1326 1327 1328 1329 1330 1331 1332 1333 1334 1335 1336 1337 1338 1339 1340 1341 1342 1343 1344 1345 1346 1347 1348 1349 1350 1351 1352 1353 1354 1355 1356 1357 1358 1359 1360 1361 1362 1363 1364 1365 1366 1367 1368 1369 1370 1371 1372 1373 1374 1375 1376 1377 1378 1379 1380 1381 1382 1383 1384 1385 1386 1387 1388 1389 1390 1391 1392 1393 1394 1395 1396 1397 1398 1399 1400 1401 1402 1403 1404 1405 |
<center><h2>🚀 LightRAG: Simple and Fast Retrieval-Augmented Generation</h2></center>
<div align="center">
<table border="0" width="100%">
<tr>
<td width="100" align="center">
<img src="./assets/logo.png" width="80" height="80" alt="lightrag">
</td>
<td>
<div>
<p>
<a href='https://lightrag.github.io'><img src='https://img.shields.io/badge/Project-Page-Green'></a>
<a href='https://youtu.be/oageL-1I0GE'><img src='https://badges.aleen42.com/src/youtube.svg'></a>
<a href='https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.05779'><img src='https://img.shields.io/badge/arXiv-2410.05779-b31b1b'></a>
<a href='https://learnopencv.com/lightrag'><img src='https://img.shields.io/badge/LearnOpenCV-blue'></a>
</p>
<p>
<img src='https://img.shields.io/github/stars/hkuds/lightrag?color=green&style=social' />
<img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/python-3.10-blue">
<a href="https://pypi.org/project/lightrag-hku/"><img src="https://img.shields.io/pypi/v/lightrag-hku.svg"></a>
<a href="https://pepy.tech/project/lightrag-hku"><img src="https://static.pepy.tech/badge/lightrag-hku/month"></a>
</p>
<p>
<a href='https://discord.gg/yF2MmDJyGJ'><img src='https://discordapp.com/api/guilds/1296348098003734629/widget.png?style=shield'></a>
<a href='https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG/issues/285'><img src='https://img.shields.io/badge/群聊-wechat-green'></a>
</p>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<img src="./README.assets/b2aaf634151b4706892693ffb43d9093.png" width="800" alt="LightRAG Diagram">
</div>
## 🎉 News
- [X] [2025.03.18]🎯📢LightRAG now supports citation functionality.
- [X] [2025.02.05]🎯📢Our team has released [VideoRAG](https://github.com/HKUDS/VideoRAG) understanding extremely long-context videos.
- [X] [2025.01.13]🎯📢Our team has released [MiniRAG](https://github.com/HKUDS/MiniRAG) making RAG simpler with small models.
- [X] [2025.01.06]🎯📢You can now [use PostgreSQL for Storage](#using-postgresql-for-storage).
- [X] [2024.12.31]🎯📢LightRAG now supports [deletion by document ID](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG?tab=readme-ov-file#delete).
- [X] [2024.11.25]🎯📢LightRAG now supports seamless integration of [custom knowledge graphs](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG?tab=readme-ov-file#insert-custom-kg), empowering users to enhance the system with their own domain expertise.
- [X] [2024.11.19]🎯📢A comprehensive guide to LightRAG is now available on [LearnOpenCV](https://learnopencv.com/lightrag). Many thanks to the blog author.
- [X] [2024.11.12]🎯📢LightRAG now supports [Oracle Database 23ai for all storage types (KV, vector, and graph)](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG/blob/main/examples/lightrag_oracle_demo.py).
- [X] [2024.11.11]🎯📢LightRAG now supports [deleting entities by their names](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG?tab=readme-ov-file#delete).
- [X] [2024.11.09]🎯📢Introducing the [LightRAG Gui](https://lightrag-gui.streamlit.app), which allows you to insert, query, visualize, and download LightRAG knowledge.
- [X] [2024.11.04]🎯📢You can now [use Neo4J for Storage](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG?tab=readme-ov-file#using-neo4j-for-storage).
- [X] [2024.10.29]🎯📢LightRAG now supports multiple file types, including PDF, DOC, PPT, and CSV via `textract`.
- [X] [2024.10.20]🎯📢We've added a new feature to LightRAG: Graph Visualization.
- [X] [2024.10.18]🎯📢We've added a link to a [LightRAG Introduction Video](https://youtu.be/oageL-1I0GE). Thanks to the author!
- [X] [2024.10.17]🎯📢We have created a [Discord channel](https://discord.gg/yF2MmDJyGJ)! Welcome to join for sharing and discussions! 🎉🎉
- [X] [2024.10.16]🎯📢LightRAG now supports [Ollama models](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG?tab=readme-ov-file#quick-start)!
- [X] [2024.10.15]🎯📢LightRAG now supports [Hugging Face models](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG?tab=readme-ov-file#quick-start)!
<details>
<summary style="font-size: 1.4em; font-weight: bold; cursor: pointer; display: list-item;">
Algorithm Flowchart
</summary>
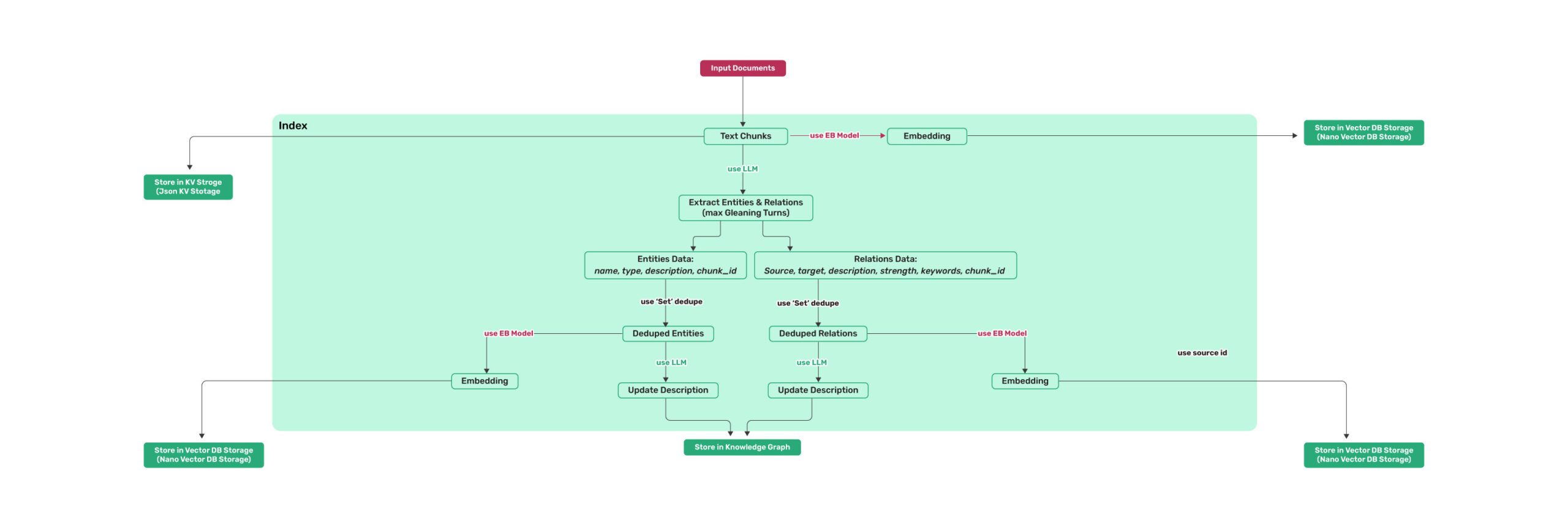
*Figure 1: LightRAG Indexing Flowchart - Img Caption : [Source](https://learnopencv.com/lightrag/)*
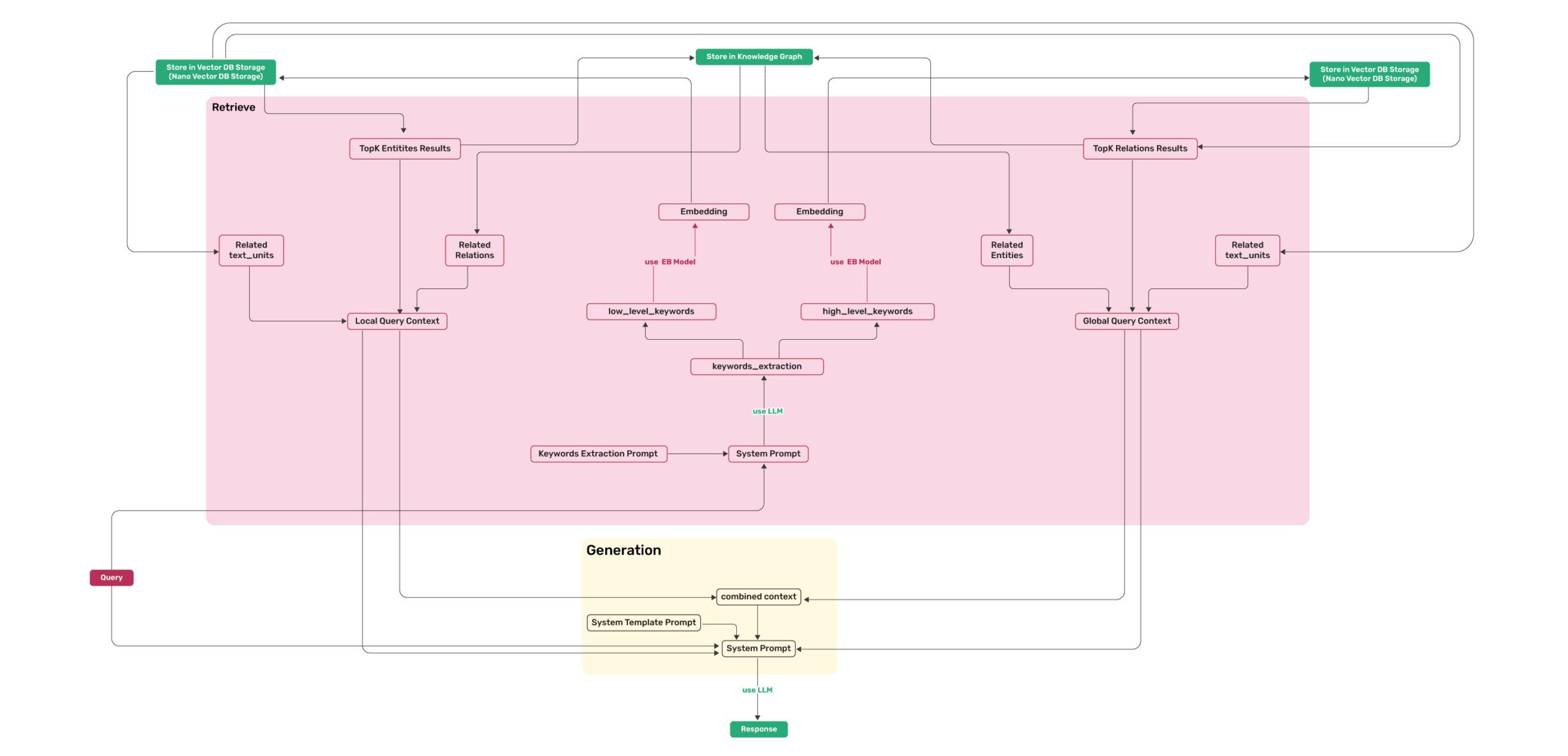
*Figure 2: LightRAG Retrieval and Querying Flowchart - Img Caption : [Source](https://learnopencv.com/lightrag/)*
</details>
## Installation
### Install LightRAG Core
* Install from source (Recommend)
```bash
cd LightRAG
pip install -e .
```
* Install from PyPI
```bash
pip install lightrag-hku
```
### Install LightRAG Server
The LightRAG Server is designed to provide Web UI and API support. The Web UI facilitates document indexing, knowledge graph exploration, and a simple RAG query interface. LightRAG Server also provide an Ollama compatible interfaces, aiming to emulate LightRAG as an Ollama chat model. This allows AI chat bot, such as Open WebUI, to access LightRAG easily.
* Install from PyPI
```bash
pip install "lightrag-hku[api]"
```
* Installation from Source
```bash
# create a Python virtual enviroment if neccesary
# Install in editable mode with API support
pip install -e ".[api]"
```
**For more information about LightRAG Server, please refer to [LightRAG Server](./lightrag/api/README.md).**
## Quick Start
* [Video demo](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g21royNJ4fw) of running LightRAG locally.
* All the code can be found in the `examples`.
* Set OpenAI API key in environment if using OpenAI models: `export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-...".`
* Download the demo text "A Christmas Carol by Charles Dickens":
```bash
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gusye1234/nano-graphrag/main/tests/mock_data.txt > ./book.txt
```
## Query
Use the below Python snippet (in a script) to initialize LightRAG and perform queries:
```python
import os
import asyncio
from lightrag import LightRAG, QueryParam
from lightrag.llm.openai import gpt_4o_mini_complete, gpt_4o_complete, openai_embed
from lightrag.kg.shared_storage import initialize_pipeline_status
from lightrag.utils import setup_logger
setup_logger("lightrag", level="INFO")
async def initialize_rag():
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir="your/path",
embedding_func=openai_embed,
llm_model_func=gpt_4o_mini_complete
)
await rag.initialize_storages()
await initialize_pipeline_status()
return rag
def main():
# Initialize RAG instance
rag = asyncio.run(initialize_rag())
# Insert text
rag.insert("Your text")
# Perform naive search
mode="naive"
# Perform local search
mode="local"
# Perform global search
mode="global"
# Perform hybrid search
mode="hybrid"
# Mix mode Integrates knowledge graph and vector retrieval.
mode="mix"
rag.query(
"What are the top themes in this story?",
param=QueryParam(mode=mode)
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
```
### Query Param
```python
class QueryParam:
mode: Literal["local", "global", "hybrid", "naive", "mix"] = "global"
"""Specifies the retrieval mode:
- "local": Focuses on context-dependent information.
- "global": Utilizes global knowledge.
- "hybrid": Combines local and global retrieval methods.
- "naive": Performs a basic search without advanced techniques.
- "mix": Integrates knowledge graph and vector retrieval. Mix mode combines knowledge graph and vector search:
- Uses both structured (KG) and unstructured (vector) information
- Provides comprehensive answers by analyzing relationships and context
- Supports image content through HTML img tags
- Allows control over retrieval depth via top_k parameter
"""
only_need_context: bool = False
"""If True, only returns the retrieved context without generating a response."""
response_type: str = "Multiple Paragraphs"
"""Defines the response format. Examples: 'Multiple Paragraphs', 'Single Paragraph', 'Bullet Points'."""
top_k: int = 60
"""Number of top items to retrieve. Represents entities in 'local' mode and relationships in 'global' mode."""
max_token_for_text_unit: int = 4000
"""Maximum number of tokens allowed for each retrieved text chunk."""
max_token_for_global_context: int = 4000
"""Maximum number of tokens allocated for relationship descriptions in global retrieval."""
max_token_for_local_context: int = 4000
"""Maximum number of tokens allocated for entity descriptions in local retrieval."""
ids: list[str] | None = None # ONLY SUPPORTED FOR PG VECTOR DBs
"""List of ids to filter the RAG."""
model_func: Callable[..., object] | None = None
"""Optional override for the LLM model function to use for this specific query.
If provided, this will be used instead of the global model function.
This allows using different models for different query modes.
"""
...
```
> default value of Top_k can be change by environment variables TOP_K.
### LLM and Embedding Injection
LightRAG requires the utilization of LLM and Embedding models to accomplish document indexing and querying tasks. During the initialization phase, it is necessary to inject the invocation methods of the relevant models into LightRAG:
<details>
<summary> <b>Using Open AI-like APIs</b> </summary>
* LightRAG also supports Open AI-like chat/embeddings APIs:
```python
async def llm_model_func(
prompt, system_prompt=None, history_messages=[], keyword_extraction=False, **kwargs
) -> str:
return await openai_complete_if_cache(
"solar-mini",
prompt,
system_prompt=system_prompt,
history_messages=history_messages,
api_key=os.getenv("UPSTAGE_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://api.upstage.ai/v1/solar",
**kwargs
)
async def embedding_func(texts: list[str]) -> np.ndarray:
return await openai_embed(
texts,
model="solar-embedding-1-large-query",
api_key=os.getenv("UPSTAGE_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://api.upstage.ai/v1/solar"
)
async def initialize_rag():
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
llm_model_func=llm_model_func,
embedding_func=EmbeddingFunc(
embedding_dim=4096,
max_token_size=8192,
func=embedding_func
)
)
await rag.initialize_storages()
await initialize_pipeline_status()
return rag
```
</details>
<details>
<summary> <b>Using Hugging Face Models</b> </summary>
* If you want to use Hugging Face models, you only need to set LightRAG as follows:
See `lightrag_hf_demo.py`
```python
# Initialize LightRAG with Hugging Face model
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
llm_model_func=hf_model_complete, # Use Hugging Face model for text generation
llm_model_name='meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct', # Model name from Hugging Face
# Use Hugging Face embedding function
embedding_func=EmbeddingFunc(
embedding_dim=384,
max_token_size=5000,
func=lambda texts: hf_embed(
texts,
tokenizer=AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"),
embed_model=AutoModel.from_pretrained("sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
)
),
)
```
</details>
<details>
<summary> <b>Using Ollama Models</b> </summary>
**Overview**
If you want to use Ollama models, you need to pull model you plan to use and embedding model, for example `nomic-embed-text`.
Then you only need to set LightRAG as follows:
```python
# Initialize LightRAG with Ollama model
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
llm_model_func=ollama_model_complete, # Use Ollama model for text generation
llm_model_name='your_model_name', # Your model name
# Use Ollama embedding function
embedding_func=EmbeddingFunc(
embedding_dim=768,
max_token_size=8192,
func=lambda texts: ollama_embed(
texts,
embed_model="nomic-embed-text"
)
),
)
```
* **Increasing context size**
In order for LightRAG to work context should be at least 32k tokens. By default Ollama models have context size of 8k. You can achieve this using one of two ways:
* **Increasing the `num_ctx` parameter in Modelfile**
1. Pull the model:
```bash
ollama pull qwen2
```
2. Display the model file:
```bash
ollama show --modelfile qwen2 > Modelfile
```
3. Edit the Modelfile by adding the following line:
```bash
PARAMETER num_ctx 32768
```
4. Create the modified model:
```bash
ollama create -f Modelfile qwen2m
```
* **Setup `num_ctx` via Ollama API**
Tiy can use `llm_model_kwargs` param to configure ollama:
```python
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
llm_model_func=ollama_model_complete, # Use Ollama model for text generation
llm_model_name='your_model_name', # Your model name
llm_model_kwargs={"options": {"num_ctx": 32768}},
# Use Ollama embedding function
embedding_func=EmbeddingFunc(
embedding_dim=768,
max_token_size=8192,
func=lambda texts: ollama_embedding(
texts,
embed_model="nomic-embed-text"
)
),
)
```
* **Low RAM GPUs**
In order to run this experiment on low RAM GPU you should select small model and tune context window (increasing context increase memory consumption). For example, running this ollama example on repurposed mining GPU with 6Gb of RAM required to set context size to 26k while using `gemma2:2b`. It was able to find 197 entities and 19 relations on `book.txt`.
</details>
<details>
<summary> <b>LlamaIndex</b> </summary>
LightRAG supports integration with LlamaIndex (`llm/llama_index_impl.py`):
- Integrates with OpenAI and other providers through LlamaIndex
- See [LlamaIndex Documentation](lightrag/llm/Readme.md) for detailed setup and examples
**Example Usage**
```python
# Using LlamaIndex with direct OpenAI access
import asyncio
from lightrag import LightRAG
from lightrag.llm.llama_index_impl import llama_index_complete_if_cache, llama_index_embed
from llama_index.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbedding
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
from lightrag.kg.shared_storage import initialize_pipeline_status
from lightrag.utils import setup_logger
# Setup log handler for LightRAG
setup_logger("lightrag", level="INFO")
async def initialize_rag():
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir="your/path",
llm_model_func=llama_index_complete_if_cache, # LlamaIndex-compatible completion function
embedding_func=EmbeddingFunc( # LlamaIndex-compatible embedding function
embedding_dim=1536,
max_token_size=8192,
func=lambda texts: llama_index_embed(texts, embed_model=embed_model)
),
)
await rag.initialize_storages()
await initialize_pipeline_status()
return rag
def main():
# Initialize RAG instance
rag = asyncio.run(initialize_rag())
with open("./book.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
rag.insert(f.read())
# Perform naive search
print(
rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(mode="naive"))
)
# Perform local search
print(
rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(mode="local"))
)
# Perform global search
print(
rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(mode="global"))
)
# Perform hybrid search
print(
rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(mode="hybrid"))
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
```
**For detailed documentation and examples, see:**
- [LlamaIndex Documentation](lightrag/llm/Readme.md)
- [Direct OpenAI Example](examples/lightrag_llamaindex_direct_demo.py)
- [LiteLLM Proxy Example](examples/lightrag_llamaindex_litellm_demo.py)
### Conversation History Support
LightRAG now supports multi-turn dialogue through the conversation history feature. Here's how to use it:
```python
# Create conversation history
conversation_history = [
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the main character's attitude towards Christmas?"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "At the beginning of the story, Ebenezer Scrooge has a very negative attitude towards Christmas..."},
{"role": "user", "content": "How does his attitude change?"}
]
# Create query parameters with conversation history
query_param = QueryParam(
mode="mix", # or any other mode: "local", "global", "hybrid"
conversation_history=conversation_history, # Add the conversation history
history_turns=3 # Number of recent conversation turns to consider
)
# Make a query that takes into account the conversation history
response = rag.query(
"What causes this change in his character?",
param=query_param
)
```
### Custom Prompt Support
LightRAG now supports custom prompts for fine-tuned control over the system's behavior. Here's how to use it:
```python
# Create query parameters
query_param = QueryParam(
mode="hybrid", # or other mode: "local", "global", "hybrid", "mix" and "naive"
)
# Example 1: Using the default system prompt
response_default = rag.query(
"What are the primary benefits of renewable energy?",
param=query_param
)
print(response_default)
# Example 2: Using a custom prompt
custom_prompt = """
You are an expert assistant in environmental science. Provide detailed and structured answers with examples.
---Conversation History---
{history}
---Knowledge Base---
{context_data}
---Response Rules---
- Target format and length: {response_type}
"""
response_custom = rag.query(
"What are the primary benefits of renewable energy?",
param=query_param,
system_prompt=custom_prompt # Pass the custom prompt
)
print(response_custom)
```
### Separate Keyword Extraction
We've introduced a new function `query_with_separate_keyword_extraction` to enhance the keyword extraction capabilities. This function separates the keyword extraction process from the user's prompt, focusing solely on the query to improve the relevance of extracted keywords.
**How It Works?**
The function operates by dividing the input into two parts:
- `User Query`
- `Prompt`
It then performs keyword extraction exclusively on the `user query`. This separation ensures that the extraction process is focused and relevant, unaffected by any additional language in the `prompt`. It also allows the `prompt` to serve purely for response formatting, maintaining the intent and clarity of the user's original question.
**Usage Example**
This `example` shows how to tailor the function for educational content, focusing on detailed explanations for older students.
```python
rag.query_with_separate_keyword_extraction(
query="Explain the law of gravity",
prompt="Provide a detailed explanation suitable for high school students studying physics.",
param=QueryParam(mode="hybrid")
)
```
### Insert Custom KG
```python
custom_kg = {
"chunks": [
{
"content": "Alice and Bob are collaborating on quantum computing research.",
"source_id": "doc-1"
}
],
"entities": [
{
"entity_name": "Alice",
"entity_type": "person",
"description": "Alice is a researcher specializing in quantum physics.",
"source_id": "doc-1"
},
{
"entity_name": "Bob",
"entity_type": "person",
"description": "Bob is a mathematician.",
"source_id": "doc-1"
},
{
"entity_name": "Quantum Computing",
"entity_type": "technology",
"description": "Quantum computing utilizes quantum mechanical phenomena for computation.",
"source_id": "doc-1"
}
],
"relationships": [
{
"src_id": "Alice",
"tgt_id": "Bob",
"description": "Alice and Bob are research partners.",
"keywords": "collaboration research",
"weight": 1.0,
"source_id": "doc-1"
},
{
"src_id": "Alice",
"tgt_id": "Quantum Computing",
"description": "Alice conducts research on quantum computing.",
"keywords": "research expertise",
"weight": 1.0,
"source_id": "doc-1"
},
{
"src_id": "Bob",
"tgt_id": "Quantum Computing",
"description": "Bob researches quantum computing.",
"keywords": "research application",
"weight": 1.0,
"source_id": "doc-1"
}
]
}
rag.insert_custom_kg(custom_kg)
```
</details>
## Insert
<details>
<summary> <b> Basic Insert </b></summary>
```python
# Basic Insert
rag.insert("Text")
```
</details>
<details>
<summary> <b> Batch Insert </b></summary>
```python
# Basic Batch Insert: Insert multiple texts at once
rag.insert(["TEXT1", "TEXT2",...])
# Batch Insert with custom batch size configuration
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
addon_params={
"insert_batch_size": 4 # Process 4 documents per batch
}
)
rag.insert(["TEXT1", "TEXT2", "TEXT3", ...]) # Documents will be processed in batches of 4
```
The `insert_batch_size` parameter in `addon_params` controls how many documents are processed in each batch during insertion. This is useful for:
- Managing memory usage with large document collections
- Optimizing processing speed
- Providing better progress tracking
- Default value is 10 if not specified
</details>
<details>
<summary> <b> Insert with ID </b></summary>
If you want to provide your own IDs for your documents, number of documents and number of IDs must be the same.
```python
# Insert single text, and provide ID for it
rag.insert("TEXT1", ids=["ID_FOR_TEXT1"])
# Insert multiple texts, and provide IDs for them
rag.insert(["TEXT1", "TEXT2",...], ids=["ID_FOR_TEXT1", "ID_FOR_TEXT2"])
```
</details>
<details>
<summary><b>Insert using Pipeline</b></summary>
The `apipeline_enqueue_documents` and `apipeline_process_enqueue_documents` functions allow you to perform incremental insertion of documents into the graph.
This is useful for scenarios where you want to process documents in the background while still allowing the main thread to continue executing.
And using a routine to process news documents.
```python
rag = LightRAG(..)
await rag.apipeline_enqueue_documents(input)
# Your routine in loop
await rag.apipeline_process_enqueue_documents(input)
```
</details>
<details>
<summary><b>Insert Multi-file Type Support</b></summary>
The `textract` supports reading file types such as TXT, DOCX, PPTX, CSV, and PDF.
```python
import textract
file_path = 'TEXT.pdf'
text_content = textract.process(file_path)
rag.insert(text_content.decode('utf-8'))
```
</details>
<details>
<summary><b>Citation Functionality</b></summary>
By providing file paths, the system ensures that sources can be traced back to their original documents.
```python
# Define documents and their file paths
documents = ["Document content 1", "Document content 2"]
file_paths = ["path/to/doc1.txt", "path/to/doc2.txt"]
# Insert documents with file paths
rag.insert(documents, file_paths=file_paths)
```
</details>
## Storage
<details>
<summary> <b>Using Neo4J for Storage</b> </summary>
* For production level scenarios you will most likely want to leverage an enterprise solution
* for KG storage. Running Neo4J in Docker is recommended for seamless local testing.
* See: https://hub.docker.com/_/neo4j
```python
export NEO4J_URI="neo4j://localhost:7687"
export NEO4J_USERNAME="neo4j"
export NEO4J_PASSWORD="password"
# Setup logger for LightRAG
setup_logger("lightrag", level="INFO")
# When you launch the project be sure to override the default KG: NetworkX
# by specifying kg="Neo4JStorage".
# Note: Default settings use NetworkX
# Initialize LightRAG with Neo4J implementation.
async def initialize_rag():
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
llm_model_func=gpt_4o_mini_complete, # Use gpt_4o_mini_complete LLM model
graph_storage="Neo4JStorage", #<-----------override KG default
)
# Initialize database connections
await rag.initialize_storages()
# Initialize pipeline status for document processing
await initialize_pipeline_status()
return rag
```
see test_neo4j.py for a working example.
</details>
<details>
<summary> <b>Using PostgreSQL for Storage</b> </summary>
For production level scenarios you will most likely want to leverage an enterprise solution. PostgreSQL can provide a one-stop solution for you as KV store, VectorDB (pgvector) and GraphDB (apache AGE).
* PostgreSQL is lightweight,the whole binary distribution including all necessary plugins can be zipped to 40MB: Ref to [Windows Release](https://github.com/ShanGor/apache-age-windows/releases/tag/PG17%2Fv1.5.0-rc0) as it is easy to install for Linux/Mac.
* If you prefer docker, please start with this image if you are a beginner to avoid hiccups (DO read the overview): https://hub.docker.com/r/shangor/postgres-for-rag
* How to start? Ref to: [examples/lightrag_zhipu_postgres_demo.py](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG/blob/main/examples/lightrag_zhipu_postgres_demo.py)
* Create index for AGE example: (Change below `dickens` to your graph name if necessary)
```sql
load 'age';
SET search_path = ag_catalog, "$user", public;
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY entity_p_idx ON dickens."Entity" (id);
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY vertex_p_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_vertex" (id);
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY directed_p_idx ON dickens."DIRECTED" (id);
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY directed_eid_idx ON dickens."DIRECTED" (end_id);
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY directed_sid_idx ON dickens."DIRECTED" (start_id);
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY directed_seid_idx ON dickens."DIRECTED" (start_id,end_id);
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY edge_p_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_edge" (id);
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY edge_sid_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_edge" (start_id);
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY edge_eid_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_edge" (end_id);
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY edge_seid_idx ON dickens."_ag_label_edge" (start_id,end_id);
create INDEX CONCURRENTLY vertex_idx_node_id ON dickens."_ag_label_vertex" (ag_catalog.agtype_access_operator(properties, '"node_id"'::agtype));
create INDEX CONCURRENTLY entity_idx_node_id ON dickens."Entity" (ag_catalog.agtype_access_operator(properties, '"node_id"'::agtype));
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY entity_node_id_gin_idx ON dickens."Entity" using gin(properties);
ALTER TABLE dickens."DIRECTED" CLUSTER ON directed_sid_idx;
-- drop if necessary
drop INDEX entity_p_idx;
drop INDEX vertex_p_idx;
drop INDEX directed_p_idx;
drop INDEX directed_eid_idx;
drop INDEX directed_sid_idx;
drop INDEX directed_seid_idx;
drop INDEX edge_p_idx;
drop INDEX edge_sid_idx;
drop INDEX edge_eid_idx;
drop INDEX edge_seid_idx;
drop INDEX vertex_idx_node_id;
drop INDEX entity_idx_node_id;
drop INDEX entity_node_id_gin_idx;
```
* Known issue of the Apache AGE: The released versions got below issue:
> You might find that the properties of the nodes/edges are empty.
> It is a known issue of the release version: https://github.com/apache/age/pull/1721
>
> You can Compile the AGE from source code and fix it.
>
</details>
<details>
<summary> <b>Using Faiss for Storage</b> </summary>
- Install the required dependencies:
```
pip install faiss-cpu
```
You can also install `faiss-gpu` if you have GPU support.
- Here we are using `sentence-transformers` but you can also use `OpenAIEmbedding` model with `3072` dimensions.
```python
async def embedding_func(texts: list[str]) -> np.ndarray:
model = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2')
embeddings = model.encode(texts, convert_to_numpy=True)
return embeddings
# Initialize LightRAG with the LLM model function and embedding function
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
llm_model_func=llm_model_func,
embedding_func=EmbeddingFunc(
embedding_dim=384,
max_token_size=8192,
func=embedding_func,
),
vector_storage="FaissVectorDBStorage",
vector_db_storage_cls_kwargs={
"cosine_better_than_threshold": 0.3 # Your desired threshold
}
)
```
</details>
## Delete
```python
# Delete Entity: Deleting entities by their names
rag.delete_by_entity("Project Gutenberg")
# Delete Document: Deleting entities and relationships associated with the document by doc id
rag.delete_by_doc_id("doc_id")
```
## Edit Entities and Relations
LightRAG now supports comprehensive knowledge graph management capabilities, allowing you to create, edit, and delete entities and relationships within your knowledge graph.
### Create Entities and Relations
```python
# Create new entity
entity = rag.create_entity("Google", {
"description": "Google is a multinational technology company specializing in internet-related services and products.",
"entity_type": "company"
})
# Create another entity
product = rag.create_entity("Gmail", {
"description": "Gmail is an email service developed by Google.",
"entity_type": "product"
})
# Create relation between entities
relation = rag.create_relation("Google", "Gmail", {
"description": "Google develops and operates Gmail.",
"keywords": "develops operates service",
"weight": 2.0
})
```
### Edit Entities and Relations
```python
# Edit an existing entity
updated_entity = rag.edit_entity("Google", {
"description": "Google is a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., founded in 1998.",
"entity_type": "tech_company"
})
# Rename an entity (with all its relationships properly migrated)
renamed_entity = rag.edit_entity("Gmail", {
"entity_name": "Google Mail",
"description": "Google Mail (formerly Gmail) is an email service."
})
# Edit a relation between entities
updated_relation = rag.edit_relation("Google", "Google Mail", {
"description": "Google created and maintains Google Mail service.",
"keywords": "creates maintains email service",
"weight": 3.0
})
```
All operations are available in both synchronous and asynchronous versions. The asynchronous versions have the prefix "a" (e.g., `acreate_entity`, `aedit_relation`).
#### Entity Operations
- **create_entity**: Creates a new entity with specified attributes
- **edit_entity**: Updates an existing entity's attributes or renames it
#### Relation Operations
- **create_relation**: Creates a new relation between existing entities
- **edit_relation**: Updates an existing relation's attributes
These operations maintain data consistency across both the graph database and vector database components, ensuring your knowledge graph remains coherent.
## Data Export Functions
### Overview
LightRAG allows you to export your knowledge graph data in various formats for analysis, sharing, and backup purposes. The system supports exporting entities, relations, and relationship data.
### Export Functions
#### Basic Usage
```python
# Basic CSV export (default format)
rag.export_data("knowledge_graph.csv")
# Specify any format
rag.export_data("output.xlsx", file_format="excel")
```
#### Different File Formats supported
```python
#Export data in CSV format
rag.export_data("graph_data.csv", file_format="csv")
# Export data in Excel sheet
rag.export_data("graph_data.xlsx", file_format="excel")
# Export data in markdown format
rag.export_data("graph_data.md", file_format="md")
# Export data in Text
rag.export_data("graph_data.txt", file_format="txt")
```
#### Additional Options
Include vector embeddings in the export (optional):
```python
rag.export_data("complete_data.csv", include_vector_data=True)
```
### Data Included in Export
All exports include:
* Entity information (names, IDs, metadata)
* Relation data (connections between entities)
* Relationship information from vector database
## Entity Merging
<details>
<summary> <b>Merge Entities and Their Relationships</b> </summary>
LightRAG now supports merging multiple entities into a single entity, automatically handling all relationships:
```python
# Basic entity merging
rag.merge_entities(
source_entities=["Artificial Intelligence", "AI", "Machine Intelligence"],
target_entity="AI Technology"
)
```
With custom merge strategy:
```python
# Define custom merge strategy for different fields
rag.merge_entities(
source_entities=["John Smith", "Dr. Smith", "J. Smith"],
target_entity="John Smith",
merge_strategy={
"description": "concatenate", # Combine all descriptions
"entity_type": "keep_first", # Keep the entity type from the first entity
"source_id": "join_unique" # Combine all unique source IDs
}
)
```
With custom target entity data:
```python
# Specify exact values for the merged entity
rag.merge_entities(
source_entities=["New York", "NYC", "Big Apple"],
target_entity="New York City",
target_entity_data={
"entity_type": "LOCATION",
"description": "New York City is the most populous city in the United States.",
}
)
```
Advanced usage combining both approaches:
```python
# Merge company entities with both strategy and custom data
rag.merge_entities(
source_entities=["Microsoft Corp", "Microsoft Corporation", "MSFT"],
target_entity="Microsoft",
merge_strategy={
"description": "concatenate", # Combine all descriptions
"source_id": "join_unique" # Combine source IDs
},
target_entity_data={
"entity_type": "ORGANIZATION",
}
)
```
When merging entities:
* All relationships from source entities are redirected to the target entity
* Duplicate relationships are intelligently merged
* Self-relationships (loops) are prevented
* Source entities are removed after merging
* Relationship weights and attributes are preserved
</details>
## Cache
<details>
<summary> <b>Clear Cache</b> </summary>
You can clear the LLM response cache with different modes:
```python
# Clear all cache
await rag.aclear_cache()
# Clear local mode cache
await rag.aclear_cache(modes=["local"])
# Clear extraction cache
await rag.aclear_cache(modes=["default"])
# Clear multiple modes
await rag.aclear_cache(modes=["local", "global", "hybrid"])
# Synchronous version
rag.clear_cache(modes=["local"])
```
Valid modes are:
- `"default"`: Extraction cache
- `"naive"`: Naive search cache
- `"local"`: Local search cache
- `"global"`: Global search cache
- `"hybrid"`: Hybrid search cache
- `"mix"`: Mix search cache
</details>
## LightRAG init parameters
<details>
<summary> Parameters </summary>
| **Parameter** | **Type** | **Explanation** | **Default** |
|--------------|----------|-----------------|-------------|
| **working_dir** | `str` | Directory where the cache will be stored | `lightrag_cache+timestamp` |
| **kv_storage** | `str` | Storage type for documents and text chunks. Supported types: `JsonKVStorage`, `OracleKVStorage` | `JsonKVStorage` |
| **vector_storage** | `str` | Storage type for embedding vectors. Supported types: `NanoVectorDBStorage`, `OracleVectorDBStorage` | `NanoVectorDBStorage` |
| **graph_storage** | `str` | Storage type for graph edges and nodes. Supported types: `NetworkXStorage`, `Neo4JStorage`, `OracleGraphStorage` | `NetworkXStorage` |
| **chunk_token_size** | `int` | Maximum token size per chunk when splitting documents | `1200` |
| **chunk_overlap_token_size** | `int` | Overlap token size between two chunks when splitting documents | `100` |
| **tiktoken_model_name** | `str` | Model name for the Tiktoken encoder used to calculate token numbers | `gpt-4o-mini` |
| **entity_extract_max_gleaning** | `int` | Number of loops in the entity extraction process, appending history messages | `1` |
| **entity_summary_to_max_tokens** | `int` | Maximum token size for each entity summary | `500` |
| **node_embedding_algorithm** | `str` | Algorithm for node embedding (currently not used) | `node2vec` |
| **node2vec_params** | `dict` | Parameters for node embedding | `{"dimensions": 1536,"num_walks": 10,"walk_length": 40,"window_size": 2,"iterations": 3,"random_seed": 3,}` |
| **embedding_func** | `EmbeddingFunc` | Function to generate embedding vectors from text | `openai_embed` |
| **embedding_batch_num** | `int` | Maximum batch size for embedding processes (multiple texts sent per batch) | `32` |
| **embedding_func_max_async** | `int` | Maximum number of concurrent asynchronous embedding processes | `16` |
| **llm_model_func** | `callable` | Function for LLM generation | `gpt_4o_mini_complete` |
| **llm_model_name** | `str` | LLM model name for generation | `meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct` |
| **llm_model_max_token_size** | `int` | Maximum token size for LLM generation (affects entity relation summaries) | `32768`(default value changed by env var MAX_TOKENS) |
| **llm_model_max_async** | `int` | Maximum number of concurrent asynchronous LLM processes | `4`(default value changed by env var MAX_ASYNC) |
| **llm_model_kwargs** | `dict` | Additional parameters for LLM generation | |
| **vector_db_storage_cls_kwargs** | `dict` | Additional parameters for vector database, like setting the threshold for nodes and relations retrieval | cosine_better_than_threshold: 0.2(default value changed by env var COSINE_THRESHOLD) |
| **enable_llm_cache** | `bool` | If `TRUE`, stores LLM results in cache; repeated prompts return cached responses | `TRUE` |
| **enable_llm_cache_for_entity_extract** | `bool` | If `TRUE`, stores LLM results in cache for entity extraction; Good for beginners to debug your application | `TRUE` |
| **addon_params** | `dict` | Additional parameters, e.g., `{"example_number": 1, "language": "Simplified Chinese", "entity_types": ["organization", "person", "geo", "event"], "insert_batch_size": 10}`: sets example limit, output language, and batch size for document processing | `example_number: all examples, language: English, insert_batch_size: 10` |
| **convert_response_to_json_func** | `callable` | Not used | `convert_response_to_json` |
| **embedding_cache_config** | `dict` | Configuration for question-answer caching. Contains three parameters: `enabled`: Boolean value to enable/disable cache lookup functionality. When enabled, the system will check cached responses before generating new answers. `similarity_threshold`: Float value (0-1), similarity threshold. When a new question's similarity with a cached question exceeds this threshold, the cached answer will be returned directly without calling the LLM. `use_llm_check`: Boolean value to enable/disable LLM similarity verification. When enabled, LLM will be used as a secondary check to verify the similarity between questions before returning cached answers. | Default: `{"enabled": False, "similarity_threshold": 0.95, "use_llm_check": False}` |
</details>
## Error Handling
<details>
<summary>Click to view error handling details</summary>
The API includes comprehensive error handling:
- File not found errors (404)
- Processing errors (500)
- Supports multiple file encodings (UTF-8 and GBK)
</details>
## LightRAG API
The LightRAG Server is designed to provide Web UI and API support. **For more information about LightRAG Server, please refer to [LightRAG Server](./lightrag/api/README.md).**
## Graph Visualization
The LightRAG Server offers a comprehensive knowledge graph visualization feature. It supports various gravity layouts, node queries, subgraph filtering, and more. **For more information about LightRAG Server, please refer to [LightRAG Server](./lightrag/api/README.md).**

## Evaluation
### Dataset
The dataset used in LightRAG can be downloaded from [TommyChien/UltraDomain](https://huggingface.co/datasets/TommyChien/UltraDomain).
### Generate Query
LightRAG uses the following prompt to generate high-level queries, with the corresponding code in `example/generate_query.py`.
<details>
<summary> Prompt </summary>
```python
Given the following description of a dataset:
{description}
Please identify 5 potential users who would engage with this dataset. For each user, list 5 tasks they would perform with this dataset. Then, for each (user, task) combination, generate 5 questions that require a high-level understanding of the entire dataset.
Output the results in the following structure:
- User 1: [user description]
- Task 1: [task description]
- Question 1:
- Question 2:
- Question 3:
- Question 4:
- Question 5:
- Task 2: [task description]
...
- Task 5: [task description]
- User 2: [user description]
...
- User 5: [user description]
...
```
</details>
### Batch Eval
To evaluate the performance of two RAG systems on high-level queries, LightRAG uses the following prompt, with the specific code available in `example/batch_eval.py`.
<details>
<summary> Prompt </summary>
```python
---Role---
You are an expert tasked with evaluating two answers to the same question based on three criteria: **Comprehensiveness**, **Diversity**, and **Empowerment**.
---Goal---
You will evaluate two answers to the same question based on three criteria: **Comprehensiveness**, **Diversity**, and **Empowerment**.
- **Comprehensiveness**: How much detail does the answer provide to cover all aspects and details of the question?
- **Diversity**: How varied and rich is the answer in providing different perspectives and insights on the question?
- **Empowerment**: How well does the answer help the reader understand and make informed judgments about the topic?
For each criterion, choose the better answer (either Answer 1 or Answer 2) and explain why. Then, select an overall winner based on these three categories.
Here is the question:
{query}
Here are the two answers:
**Answer 1:**
{answer1}
**Answer 2:**
{answer2}
Evaluate both answers using the three criteria listed above and provide detailed explanations for each criterion.
Output your evaluation in the following JSON format:
{{
"Comprehensiveness": {{
"Winner": "[Answer 1 or Answer 2]",
"Explanation": "[Provide explanation here]"
}},
"Empowerment": {{
"Winner": "[Answer 1 or Answer 2]",
"Explanation": "[Provide explanation here]"
}},
"Overall Winner": {{
"Winner": "[Answer 1 or Answer 2]",
"Explanation": "[Summarize why this answer is the overall winner based on the three criteria]"
}}
}}
```
</details>
### Overall Performance Table
| |**Agriculture**| |**CS**| |**Legal**| |**Mix**| |
|----------------------|---------------|------------|------|------------|---------|------------|-------|------------|
| |NaiveRAG|**LightRAG**|NaiveRAG|**LightRAG**|NaiveRAG|**LightRAG**|NaiveRAG|**LightRAG**|
|**Comprehensiveness**|32.4%|**67.6%**|38.4%|**61.6%**|16.4%|**83.6%**|38.8%|**61.2%**|
|**Diversity**|23.6%|**76.4%**|38.0%|**62.0%**|13.6%|**86.4%**|32.4%|**67.6%**|
|**Empowerment**|32.4%|**67.6%**|38.8%|**61.2%**|16.4%|**83.6%**|42.8%|**57.2%**|
|**Overall**|32.4%|**67.6%**|38.8%|**61.2%**|15.2%|**84.8%**|40.0%|**60.0%**|
| |RQ-RAG|**LightRAG**|RQ-RAG|**LightRAG**|RQ-RAG|**LightRAG**|RQ-RAG|**LightRAG**|
|**Comprehensiveness**|31.6%|**68.4%**|38.8%|**61.2%**|15.2%|**84.8%**|39.2%|**60.8%**|
|**Diversity**|29.2%|**70.8%**|39.2%|**60.8%**|11.6%|**88.4%**|30.8%|**69.2%**|
|**Empowerment**|31.6%|**68.4%**|36.4%|**63.6%**|15.2%|**84.8%**|42.4%|**57.6%**|
|**Overall**|32.4%|**67.6%**|38.0%|**62.0%**|14.4%|**85.6%**|40.0%|**60.0%**|
| |HyDE|**LightRAG**|HyDE|**LightRAG**|HyDE|**LightRAG**|HyDE|**LightRAG**|
|**Comprehensiveness**|26.0%|**74.0%**|41.6%|**58.4%**|26.8%|**73.2%**|40.4%|**59.6%**|
|**Diversity**|24.0%|**76.0%**|38.8%|**61.2%**|20.0%|**80.0%**|32.4%|**67.6%**|
|**Empowerment**|25.2%|**74.8%**|40.8%|**59.2%**|26.0%|**74.0%**|46.0%|**54.0%**|
|**Overall**|24.8%|**75.2%**|41.6%|**58.4%**|26.4%|**73.6%**|42.4%|**57.6%**|
| |GraphRAG|**LightRAG**|GraphRAG|**LightRAG**|GraphRAG|**LightRAG**|GraphRAG|**LightRAG**|
|**Comprehensiveness**|45.6%|**54.4%**|48.4%|**51.6%**|48.4%|**51.6%**|**50.4%**|49.6%|
|**Diversity**|22.8%|**77.2%**|40.8%|**59.2%**|26.4%|**73.6%**|36.0%|**64.0%**|
|**Empowerment**|41.2%|**58.8%**|45.2%|**54.8%**|43.6%|**56.4%**|**50.8%**|49.2%|
|**Overall**|45.2%|**54.8%**|48.0%|**52.0%**|47.2%|**52.8%**|**50.4%**|49.6%|
## Reproduce
All the code can be found in the `./reproduce` directory.
### Step-0 Extract Unique Contexts
First, we need to extract unique contexts in the datasets.
<details>
<summary> Code </summary>
```python
def extract_unique_contexts(input_directory, output_directory):
os.makedirs(output_directory, exist_ok=True)
jsonl_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(input_directory, '*.jsonl'))
print(f"Found {len(jsonl_files)} JSONL files.")
for file_path in jsonl_files:
filename = os.path.basename(file_path)
name, ext = os.path.splitext(filename)
output_filename = f"{name}_unique_contexts.json"
output_path = os.path.join(output_directory, output_filename)
unique_contexts_dict = {}
print(f"Processing file: {filename}")
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as infile:
for line_number, line in enumerate(infile, start=1):
line = line.strip()
if not line:
continue
try:
json_obj = json.loads(line)
context = json_obj.get('context')
if context and context not in unique_contexts_dict:
unique_contexts_dict[context] = None
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"JSON decoding error in file {filename} at line {line_number}: {e}")
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"File not found: {filename}")
continue
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred while processing file {filename}: {e}")
continue
unique_contexts_list = list(unique_contexts_dict.keys())
print(f"There are {len(unique_contexts_list)} unique `context` entries in the file {filename}.")
try:
with open(output_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as outfile:
json.dump(unique_contexts_list, outfile, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
print(f"Unique `context` entries have been saved to: {output_filename}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred while saving to the file {output_filename}: {e}")
print("All files have been processed.")
```
</details>
### Step-1 Insert Contexts
For the extracted contexts, we insert them into the LightRAG system.
<details>
<summary> Code </summary>
```python
def insert_text(rag, file_path):
with open(file_path, mode='r') as f:
unique_contexts = json.load(f)
retries = 0
max_retries = 3
while retries < max_retries:
try:
rag.insert(unique_contexts)
break
except Exception as e:
retries += 1
print(f"Insertion failed, retrying ({retries}/{max_retries}), error: {e}")
time.sleep(10)
if retries == max_retries:
print("Insertion failed after exceeding the maximum number of retries")
```
</details>
### Step-2 Generate Queries
We extract tokens from the first and the second half of each context in the dataset, then combine them as dataset descriptions to generate queries.
<details>
<summary> Code </summary>
```python
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained('gpt2')
def get_summary(context, tot_tokens=2000):
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(context)
half_tokens = tot_tokens // 2
start_tokens = tokens[1000:1000 + half_tokens]
end_tokens = tokens[-(1000 + half_tokens):1000]
summary_tokens = start_tokens + end_tokens
summary = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_string(summary_tokens)
return summary
```
</details>
### Step-3 Query
For the queries generated in Step-2, we will extract them and query LightRAG.
<details>
<summary> Code </summary>
```python
def extract_queries(file_path):
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
data = f.read()
data = data.replace('**', '')
queries = re.findall(r'- Question \d+: (.+)', data)
return queries
```
</details>
## Star History
<a href="https://star-history.com/#HKUDS/LightRAG&Date">
<picture>
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" srcset="https://api.star-history.com/svg?repos=HKUDS/LightRAG&type=Date&theme=dark" />
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" srcset="https://api.star-history.com/svg?repos=HKUDS/LightRAG&type=Date" />
<img alt="Star History Chart" src="https://api.star-history.com/svg?repos=HKUDS/LightRAG&type=Date" />
</picture>
</a>
## Contribution
Thank you to all our contributors!
<a href="https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG/graphs/contributors">
<img src="https://contrib.rocks/image?repo=HKUDS/LightRAG" />
</a>
## 🌟Citation
```python
@article{guo2024lightrag,
title={LightRAG: Simple and Fast Retrieval-Augmented Generation},
author={Zirui Guo and Lianghao Xia and Yanhua Yu and Tu Ao and Chao Huang},
year={2024},
eprint={2410.05779},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.IR}
}
```
**Thank you for your interest in our work!**
|